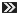All you need to know about Road Studs (Cat's Eyes)
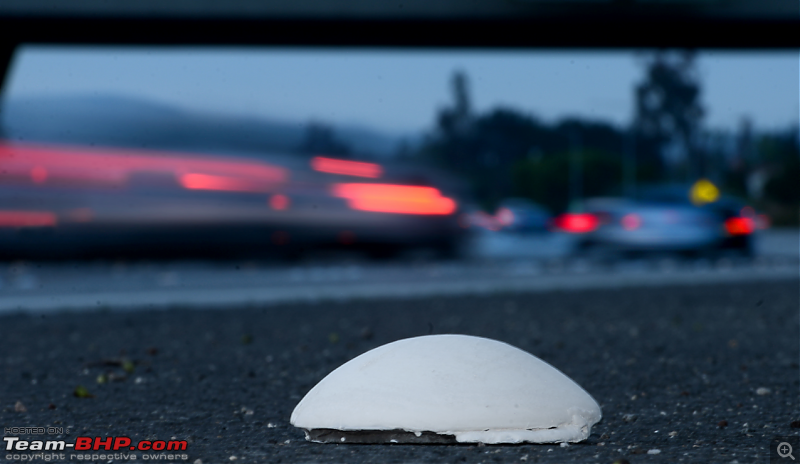
Driving along a dark road, you might have seen occasional flashes of light emitting from some devices that have been installed on the road. These devices are called road studs, or cat's eyes (due to their design) or Raised Pavement Markers. These objects include a lens or sheeting that enhances their visibility by reflecting the light from headlights of vehicles and make the road visible to the drivers. They are bonded or anchored within the road surface for lane marking and delineation for night-time visibility.
 Image Source
Image Source History
Road studs were invented British inventor Percy Shaw in 1933 and patented in the UK in 1934. In 1935. They were designed in order to help drivers follow the road in darkness or fog. The idea came to his mind after observing the manner in which cars' headlights reflected off road signs. Shaw founded a company called Reflecting Roadstuds Ltd., which was first manufacturer of road studs.
Description
Road studs come in different sizes and are available in aluminum, rigid ABS plastic or glass. They are built to be able to withstand heavy loads and severe impacts. They can have reflectors on either one, both or all sides. The reflectors can be or various colours depending upon their intended use. The most common ones we get to see in India are white, yellow and red.
Of late, more advanced road studs have been introduced. These feature solar-powered LEDs instead. They can run on a single charge for many days. Of course, these are also more expensive than the regular reflector version.
Types of Road Studs
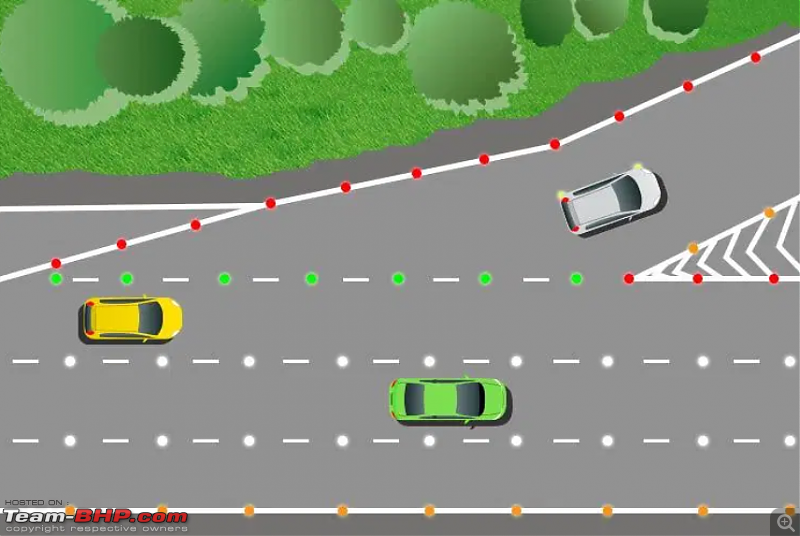
Aluminium Road Studs:
As the name suggests, aluminium road studs have aluminium casings with reflective objects installed within them. These are strong and durable. They are suitable to install in the middle of the road.
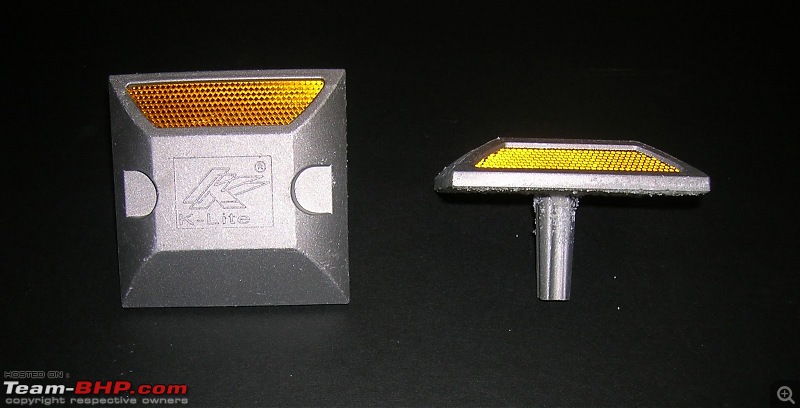 Image Source Plastic Road Studs:
Image Source Plastic Road Studs:
Plastic road studs are made of plastic and have reflective materials. They are not as strong as aluminium road studs and less durable as well. They can be used on the centre line of a road, sides of a highway and bridges.
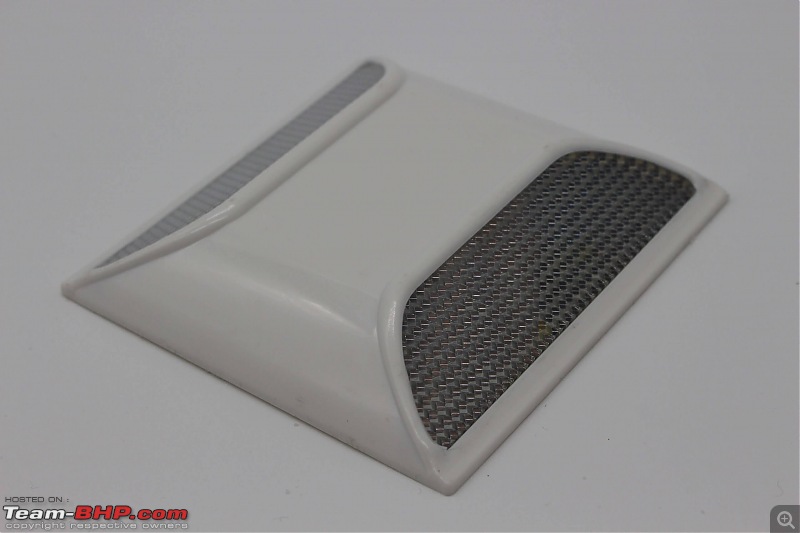 Image Source Glass Road Studs:
Image Source Glass Road Studs:
Solid glass road studs are made of hardened safety glass. The bottom of the reflector is covered with a coating, providing the reflective effect. The incoming light is bounced back by a reflector in the exact same direction from which it came, for 360 degrees. This means the reflector reflects the light of vehicles from every angle back to the road users.
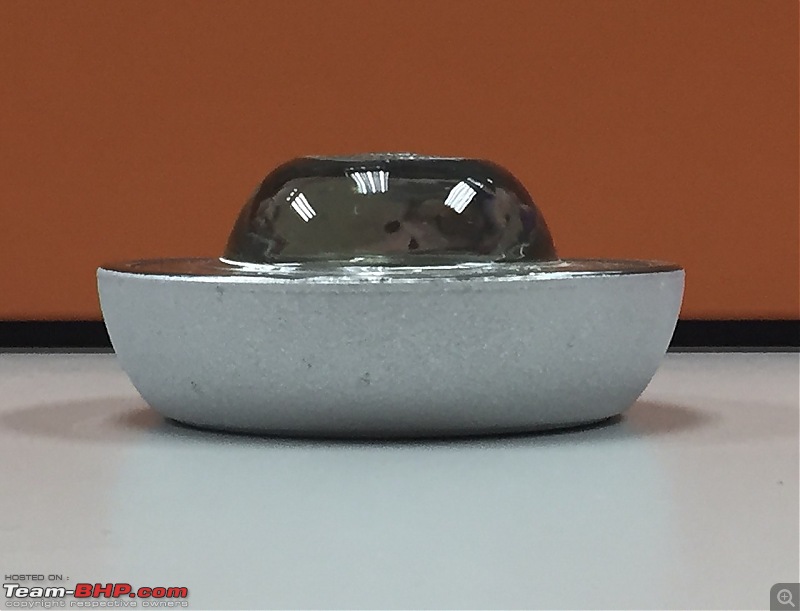 Image Source LED Road Studs:
Image Source LED Road Studs:
LED road studs come with a solar panel on the top and a battery they gets charged by sunlight during the daytime. At night their LEDs start emitting light. They may or may not have small reflectors, but because of the bright LEDs, they are a lot more visible. They can easily be viewed from a longer distance than other types of road studs.
 Image Source
Image Source  Image Source
Image Source Reflective Materials
Reflective sheet and Plastic Reflectors:
These are suitable for short term projects as they have a short life-span and lose their reflective properties with time. Reflectors with these materials are more suitable in places where road works are carried out on a more frequent basis compared to others.
Glass Beads:
Glass Beads are more durable than reflective sheets and plastic reflectors. They require less frequent replacement and are more suitable for long term projects.
Purpose
Road studs are among the most important devices in preventing cars from running off the road or their lanes and making our roads safer. They reflect the light from a car's headlights to allow the driver to observe the curves and corners of the road from a distance. Even in the dark, the driver is easily able to see the road alignments, ends, and corners of the road and judge where to turn, what lane of the road to adopt and in turn, drive safely. This makes studs extremely useful on poorly lit roads. They provide effective night guidance even under adverse weather conditions.
Additionally, these studs serve as lane markers. When a car runs over them, bumps are transmitted into the cabin which the occupants will always notice. That means that if the car is drifting from one lane to another, the driver will be alerted and can take corrective action.
You will also find road studs installed at pedestrian crossings. These give the driver of an approaching vehicle a clear indication of the pedestrian crossing.
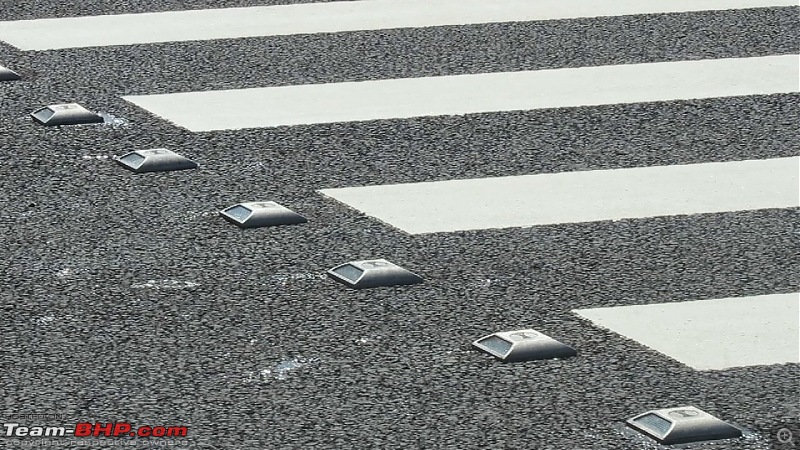 Image Source
Image Source
The rules of distance to be maintained between two reflective road studs varies from country to country. In India, the distance between two reflective cat's eyes on the road is determined by the type of road. On highways, it is usually 9 m - 18 m and depends on the radius of the horizontal/vertical curve of the section of the road.
Pros of Road Studs
- They act as guidelines telling the drivers where and how the road turns.
- They work and provide visibility during the day or night, regardless of the weather.
- They tell the driver that his car is drifting into another lane by providing audible and tactile feedback.
- Road studs on the edge of the road highlight and help drivers judge the boundaries of the road. This reduces the chances of vehicles running off the road.
- They do not need electricity. They have either reflectors or solar-powered LEDs, which means there is no electricity consumption.
- They act as speed breakers. Elevated road studs are installed to reduce or control the speed of vehicles, particularly on city roads.
Cons of Road Studs
- They are expensive to install and replace. Painting lines to mark lanes and the edges of the road is cheaper.
- Poor installation of road studs can make them loose, which may cause accidents.
- Road studs with bright blinking solar-powered LED can create a flickering effect that is picked up by the brain and causes photosensitive epilepsy.
- Vehicles create a noise when they go over road studs. This can be annoying for occupants of the vehicles and other road users.
- Road studs cannot be installed on unpaved roads.
Here's a video showing how road studs are installed:
Sources:
NK Roadstud,
Civil Engineering Bible,
3M India
 (67)
Thanks
(67)
Thanks

 (2)
Thanks
(2)
Thanks

 (7)
Thanks
(7)
Thanks
 (11)
Thanks
(11)
Thanks
 (2)
Thanks
(2)
Thanks
 (2)
Thanks
(2)
Thanks
 (16)
Thanks
(16)
Thanks
 (7)
Thanks
(7)
Thanks
 (1)
Thanks
(1)
Thanks
 (3)
Thanks
(3)
Thanks

 (7)
Thanks
(7)
Thanks
 (1)
Thanks
(1)
Thanks
 (1)
Thanks
(1)
Thanks
 (1)
Thanks
(1)
Thanks
 (1)
Thanks
(1)
Thanks