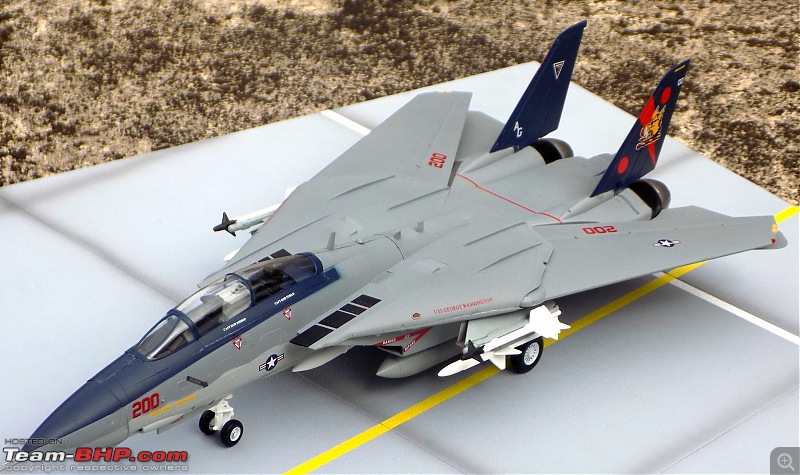
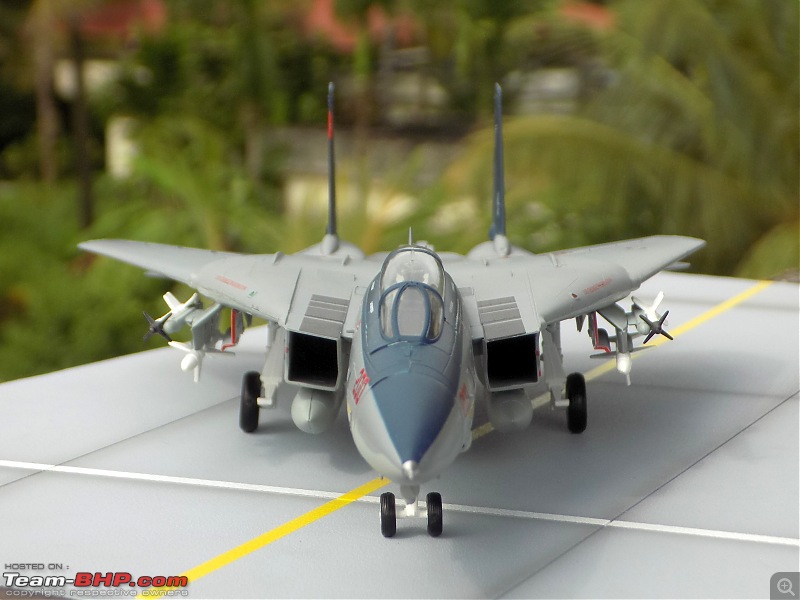
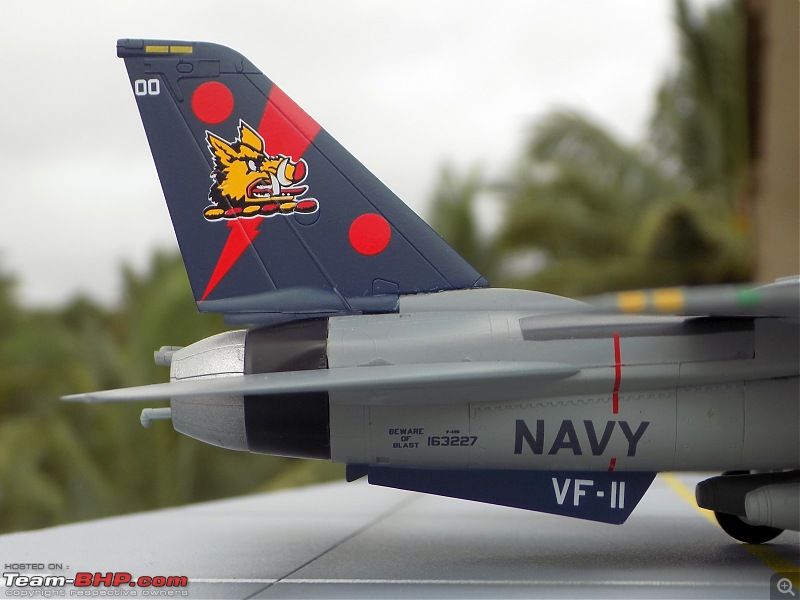
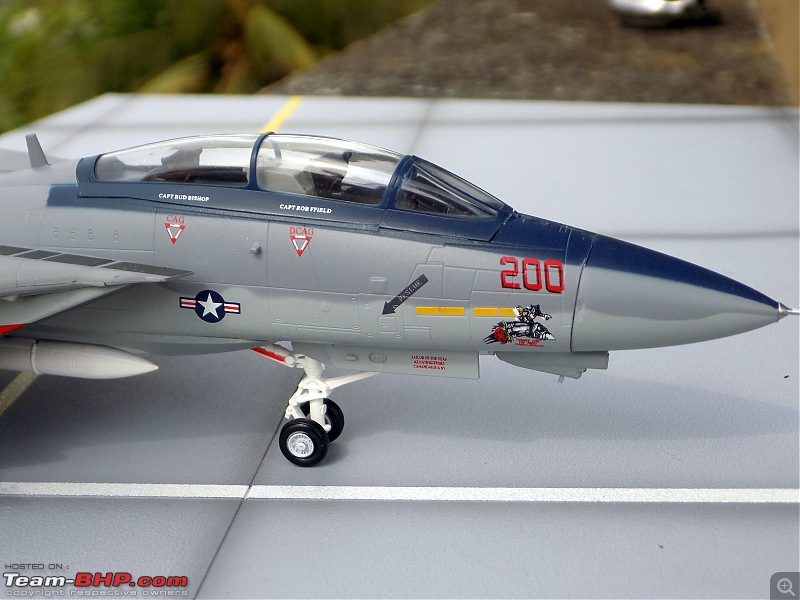
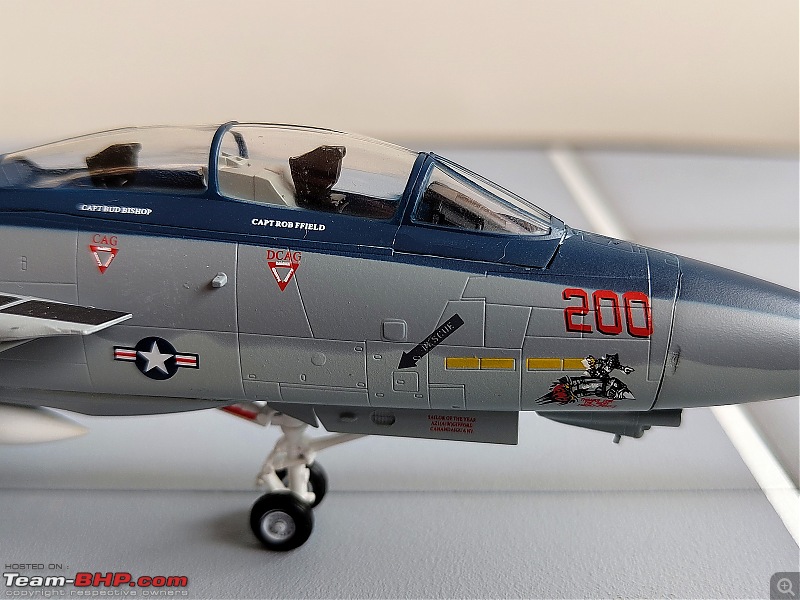
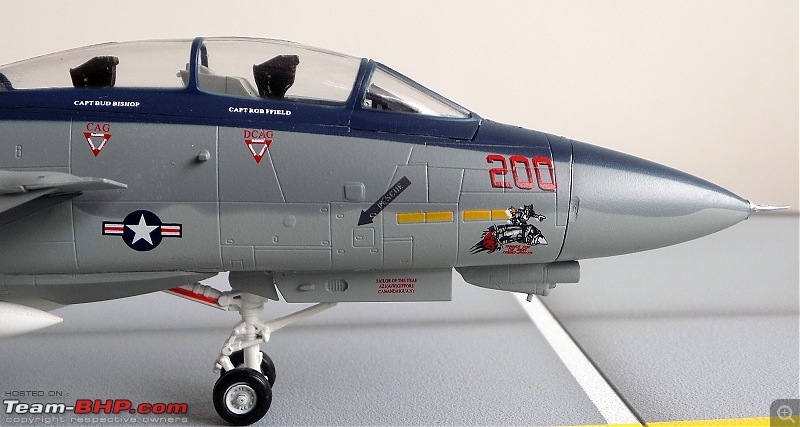
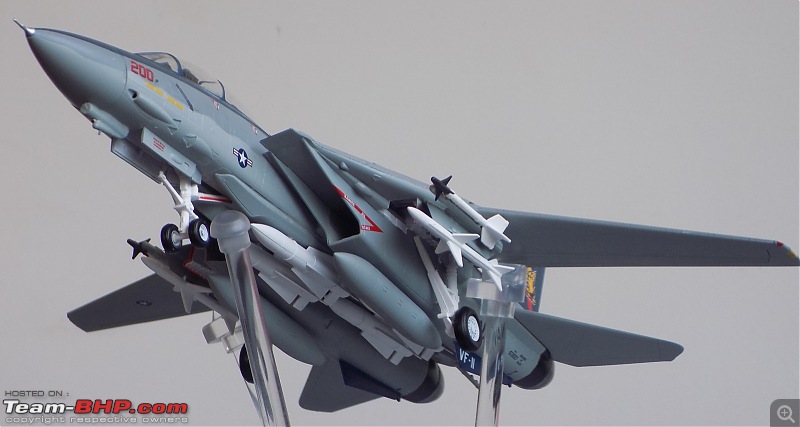
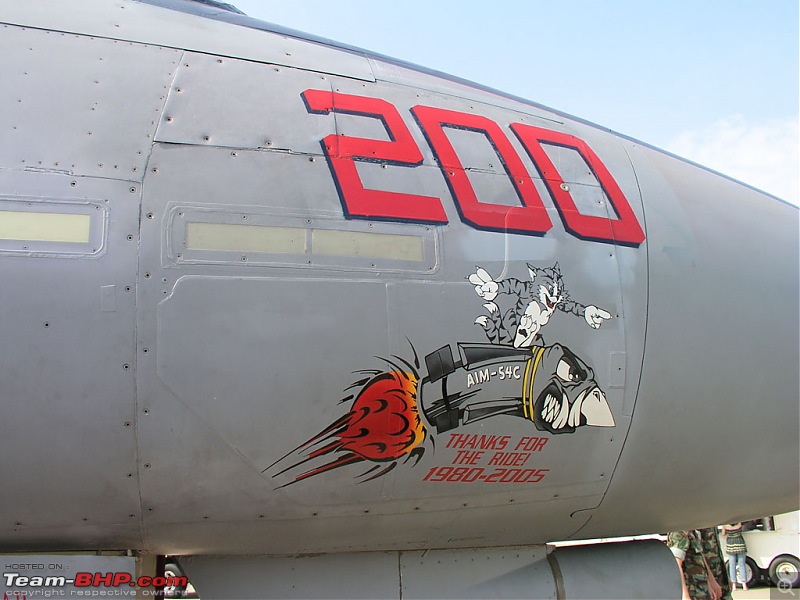
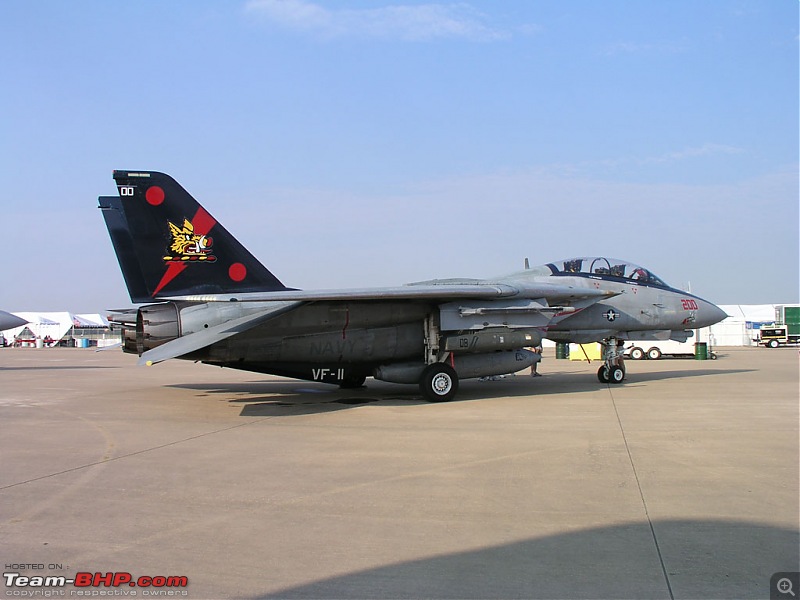
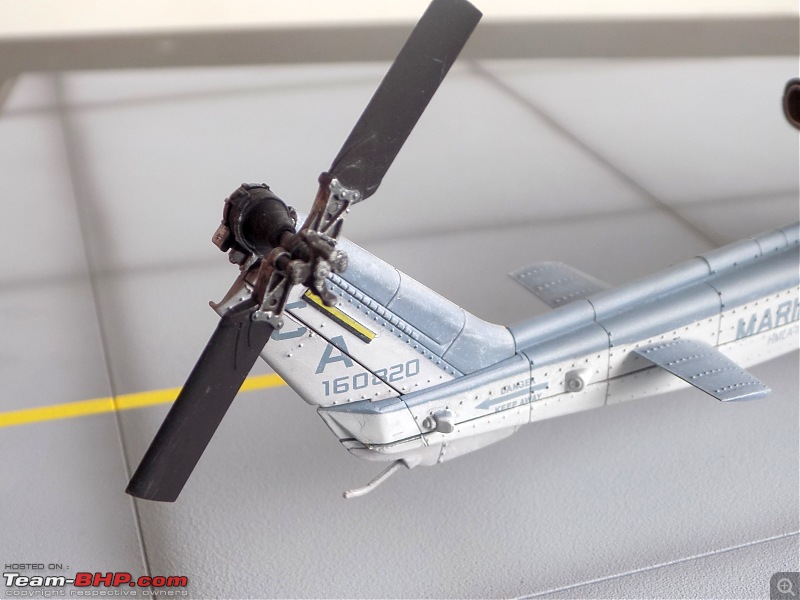
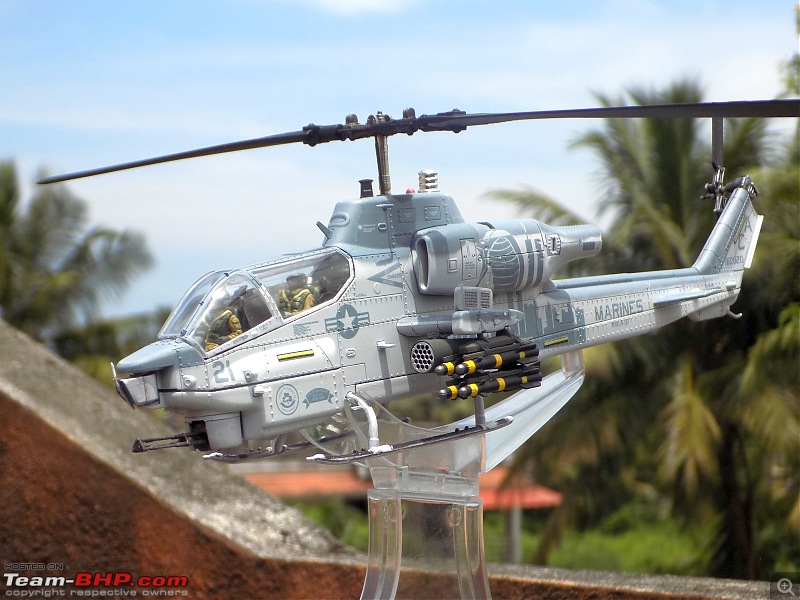
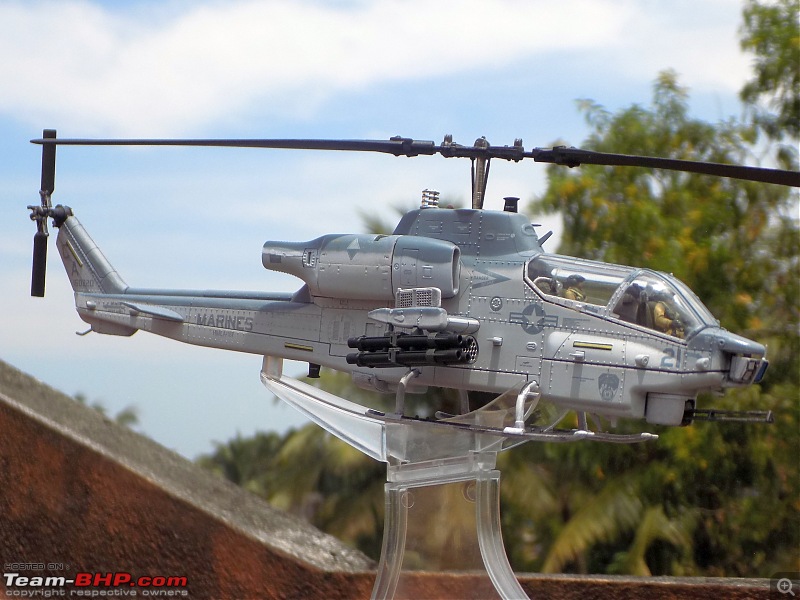
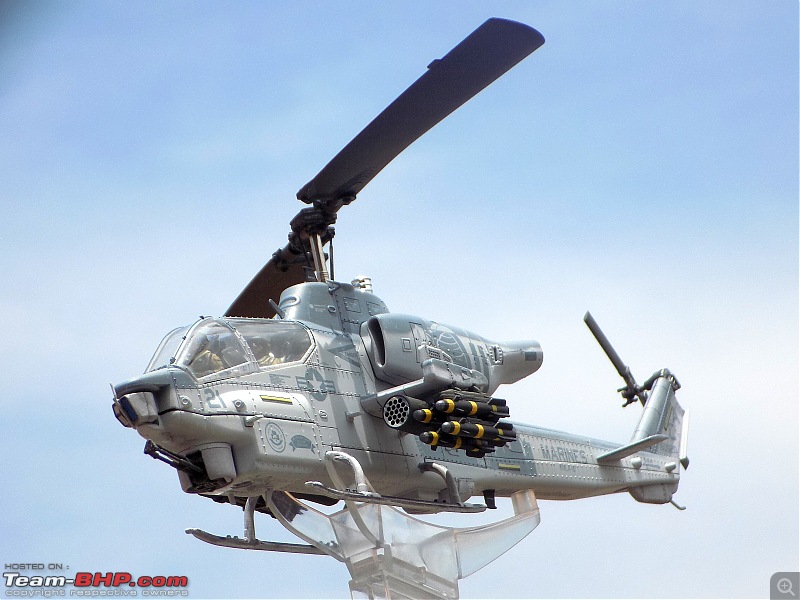
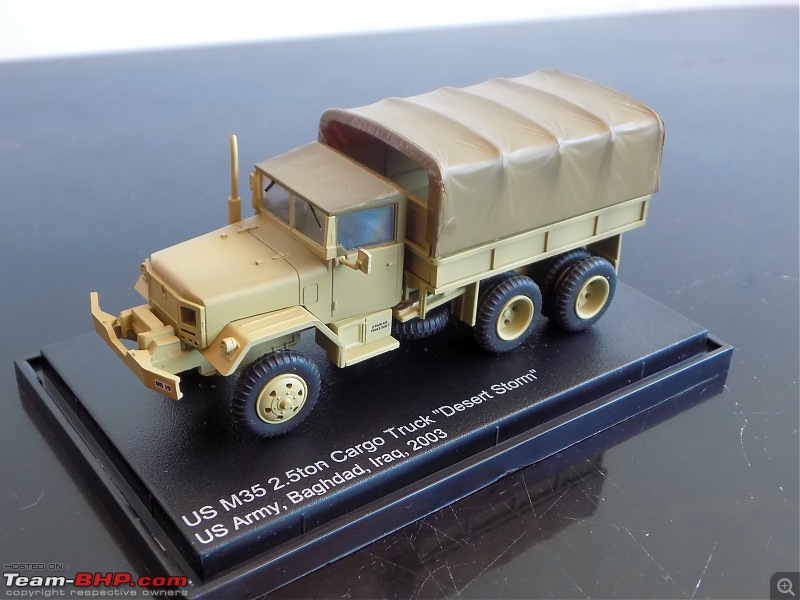
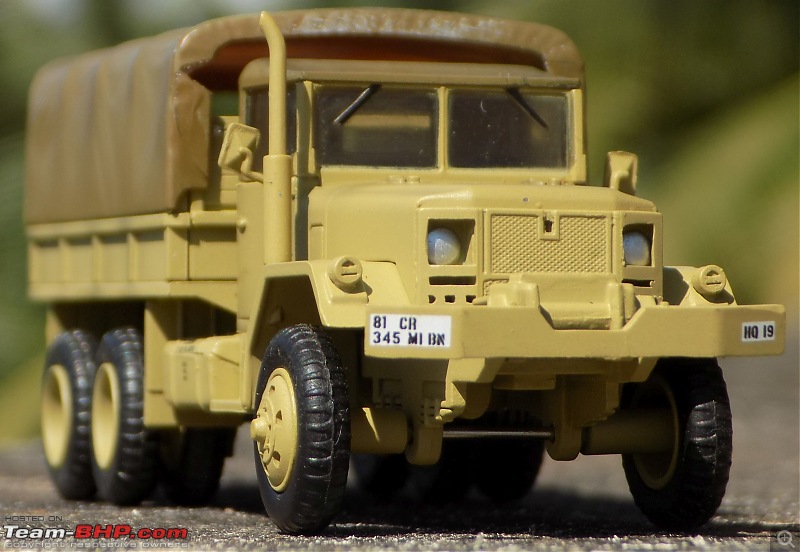
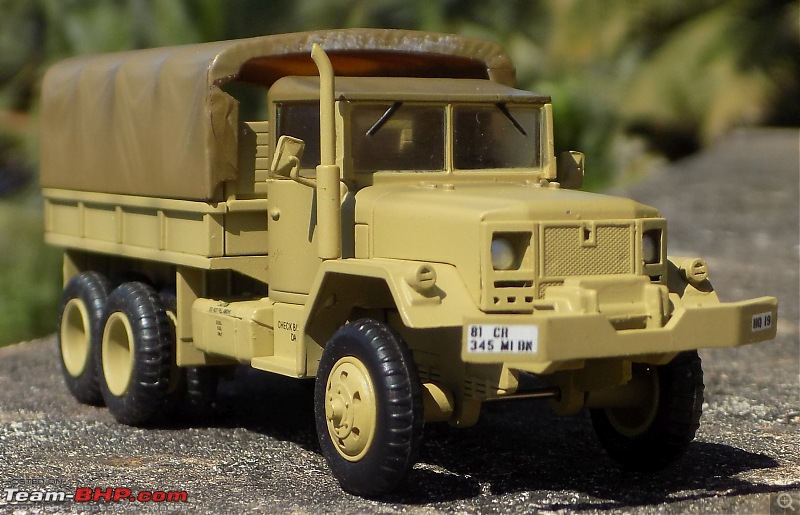
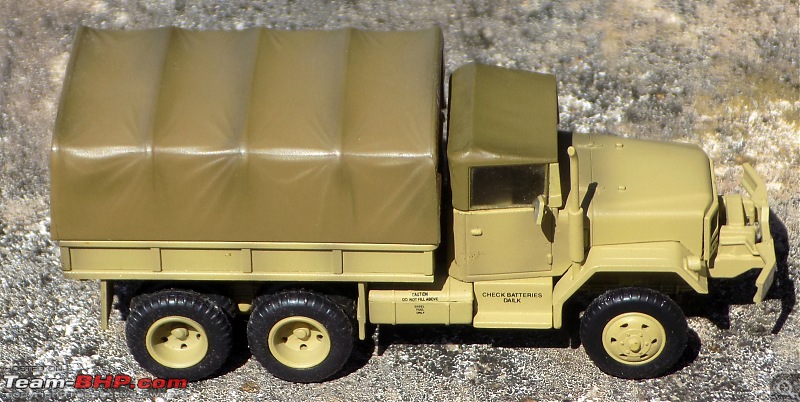
1:48 Bell AH-1W Super Cobra - HMLA 167 "Warriors", United States Marine Corps, BuNo. 160820, 9/11 tribute markings, Camp Bastion, Afghanistan, Dec 2012 (Forces of Valor)
The Bell AH-1W Super Cobra is a twin-engined, twin seat attack helicopter The twin engine Cobra family, itself part of the larger UH-1 Huey family, includes the AH-1J Sea Cobra, AH-1T Improved Sea Cobra, and the AH-1W Super Cobra. The AH-1W was the backbone of the United States Marine Corps attack helicopter fleet for decades until it was replaced by the next generation Bell AH-1Z Viper.
The AH-1 Super Cobra was based on the US Army's single-engine AH-1G Cobra attack helicopter. The pilot sits in the rear cockpit while the Gunner sits in the front cockpit. The U.S. Marine Corps was very interested in the AH-1G Cobra, but it preferred a twin-engine version for improved safety in over-water operations, and also wanted a more potent turret-mounted weapon. At first, the US Department of Defense had balked at providing the Marines with a twin-engine version of the Cobra, in the belief that commonality with US Army AH-1Gs outweighed the advantages of a different engine fit. However, the Marines won out and awarded Bell a contract for 49 twin-engine AH-1J Sea Cobras in May 1968. As an interim measure, the U.S. Army passed on 38 AH-1Gs to the Marines in 1969. The AH-1J also received a more powerful gun turret. It featured a three-barrel 20 mm XM197 cannon based on the six-barrel M61 Vulcan cannon.
The Marine Corps requested greater load carrying capability in high temperatures for the Cobra in the 1970s. Bell used systems from its Model 309 to develop the AH-1T. This version had a lengthened tail boom and fuselage with an upgraded transmission and engines from the 309. Bell designed the AH-1T to be more reliable and easier to maintain in the field. The version was given full TOW missile capability with targeting system and other sensors. An advanced version, known as the AH-1T+ with more powerful T700-GE-700 engines and advanced avionics was proposed to Iran in the late 1970s, but the overthrow of the Shah of Iran resulted in the sale being canceled
In the early 1980s, the U.S. Marine Corps sought a new navalized helicopter, but it was denied funding to buy the AH-64 Apache by Congress in 1981. The Marines in turn pursued a more powerful version of the AH-1T. Other changes included modified fire control systems to carry and fire AIM-9 Sidewinder and AGM-114 Hellfire missiles. The new version was funded by Congress and received the AH-1W designation. Deliveries of AH-1W Super Cobras started in March 1986 and totaled 179 new-built helicopters plus 43 upgrades of AH-1Ts.
The AH-1W variant entered service with the USMC in 1986. The "Whiskey Cobra", as it was called, was the first day/night version pf the Super Cobra family with more powerful engines and advanced weapons capability.
AH-1W in action
During the Gulf War, 78 Marine Super Cobras deployed, and flew a total of 1,273 sorties in Iraq with no combat losses. However, three AH-1s were lost to accidents during and after the combat operations. The AH-1W units were credited with destroying 97 tanks, 104 armored personnel carriers and vehicles, and two anti-aircraft artillery sites during the 100-hour ground campaign.
Marine Cobras provided support for the U.S. humanitarian intervention in Somalia, during Operation Restore Hope in 1992–93. They were also employed during the U.S. invasion of Haiti in 1994. USMC Cobras were used in U.S. military interventions in the former Yugoslavia in the 1990s, and two AH-1Ws assisted in the rescue of USAF Captain Scott O'Grady, after his F-16 was shot down by a SAM in June 1995.
AH-1 Cobras continue to operate with the U.S. Marine Corps. USMC Cobras were also used in operations throughout the 1990s. USMC Cobras have also served in Operation Enduring Freedom in Afghanistan and in Operation Iraqi Freedom in the conflict in Iraq. While new replacement aircraft were considered as an alternative to major upgrades of the AH-1 fleet, Marine Corps studies showed that an upgrade was the most affordable, most supportable and most effective solution for the Marine Corps light attack helicopter mission.
During the 2003 invasion of Iraq, 46 of 58 USMC Cobras took battle damage, mostly from infantry-type weapons.
On 19 September 2011, a USMC AH-1W crashed during training exercises at Camp Pendleton, California, killing the two crewmen on board. An investigation into the crash determined that it was caused by bird strike. The aircraft had collided with a red-tailed hawk, the impact damaging the pitch change link which in turn produced vibrations to the rotors so fierce that they caused the transmission and rotors to break off from the helicopter body
In late August 2016, Marine AH-1W Cobras flying from USS Wasp started flying combat missions over Sirte, Libya against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant in Libya, providing close air support for friendly militias on the ground. In the later stages of the operation, AH-1Ws flew combat missions from the deck of USS San Antonio after that ship replaced Wasp in October 2016.
In October 2020, the U.S. Marine Corps retired the AH-1W after 34 years of service, replacing it with the AH-1Z Viper. The Marines received 179 Super Cobras from 1986 to 1999 which flew 933,614 hours. the AH-1W remains in service with the Taiwan Army & Turkish Navy.
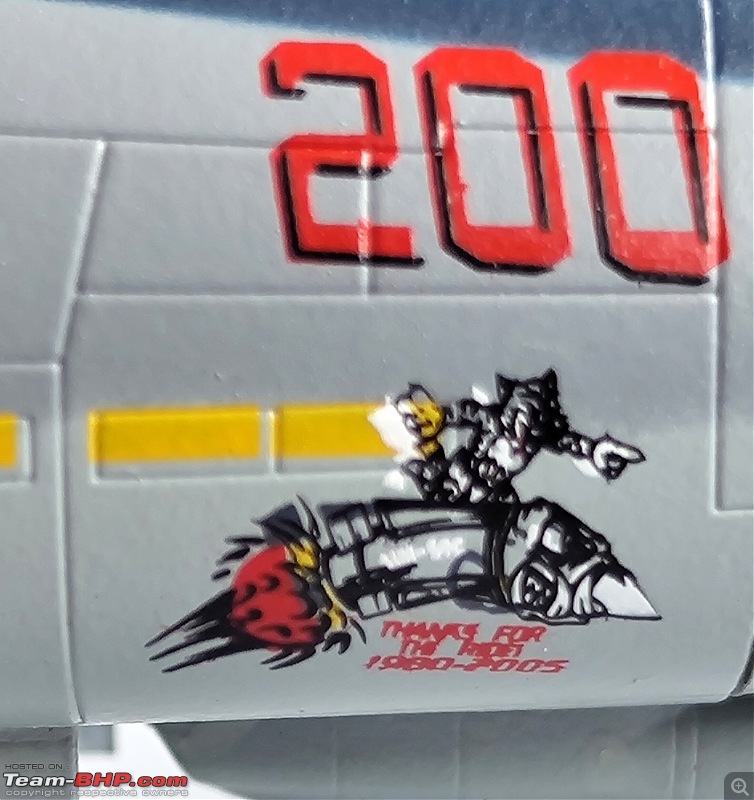
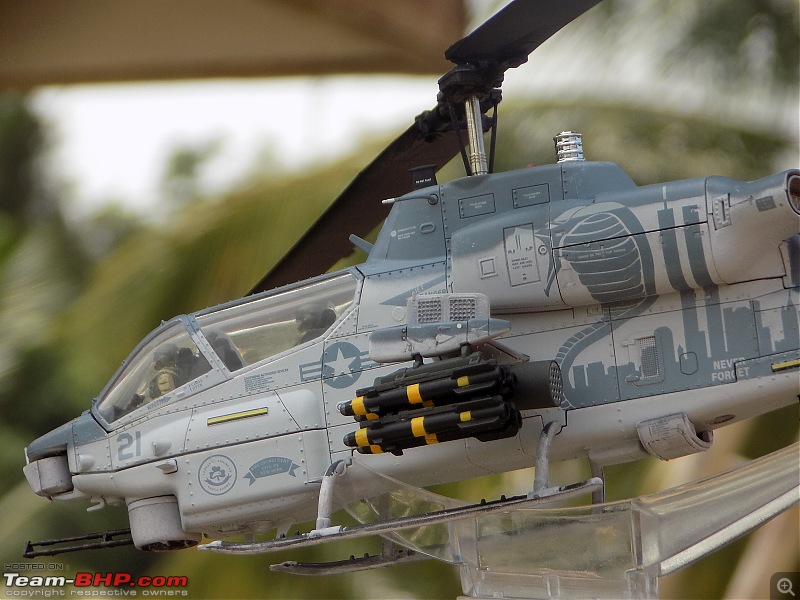
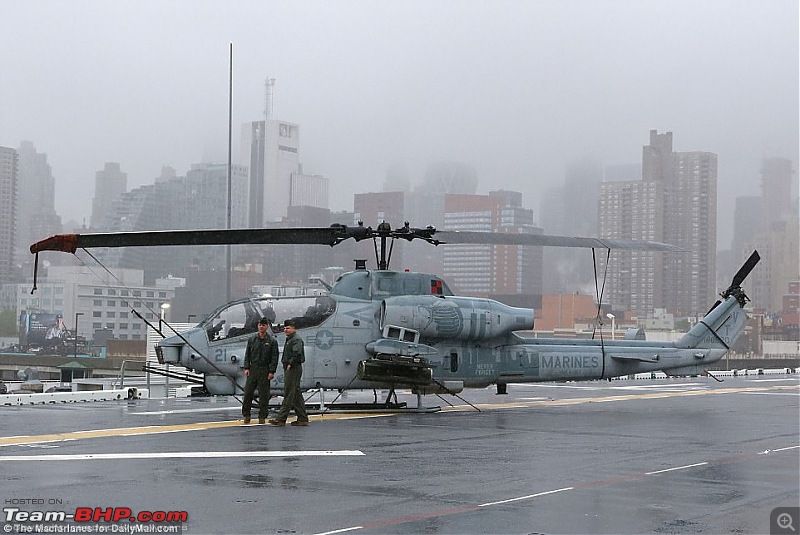
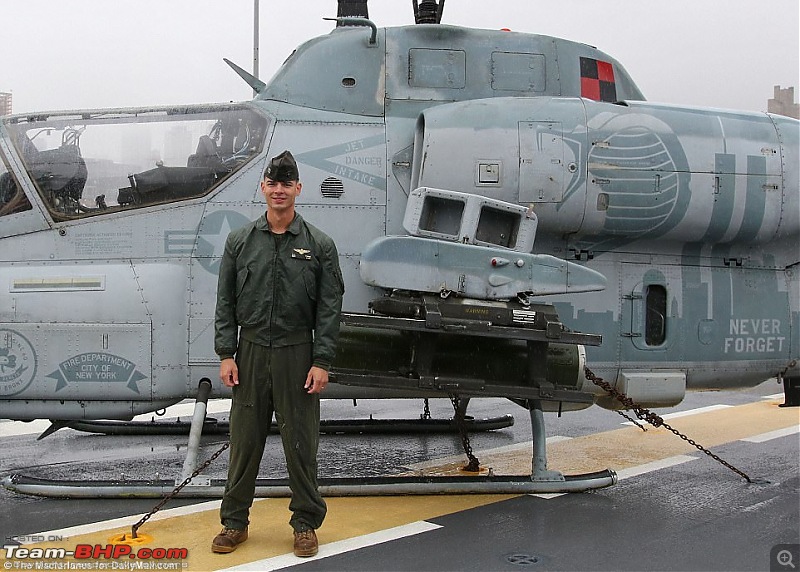
The 9/11 Tribute
The crew of this US Marine Corps AH-1W helicopter painted a stencil of the Twin Towers on its side after reading about the heroics of the New York City firefighters on 9/11.
The Super Cobra flew combat missions in Afghanistan in 2010 but were in awe at the sacrifice of the New York Fire Department on September 11 2001.They wrote the words 'Never Forget' on the side of the AH-1W Super Cobra and painted a New York Fire Department logo on it. The Cobra was deployed against the Taliban in Afghanistan when it was given the markings to pay respect to the FDNY. The Cobra is stenciled with the emblem of the FDNY's Engine 60 and Ladder 17, whose firefighters are in the South Bronx. They wear green berets in the St. Patrick's Day parade in the city
Specifications
Contractor : Bell Helicopter, Textron, Inc. (Prime), General Electric, Kollsman Inc.
Introduction date : 1986
General characteristics
Crew 2: pilot, CPG (co-pilot/gunner)
Fuselage length : 44 ft 7 in (13.6 m)
Length, rotors turning Rotor diameter : 48 ft (14.6 m)
Height: 13 ft 5 in (4.1 m)
Disc area: 530.83 ft² (168.1 m²)
Empty weight: 10,920 lb (4,953 kg)
Max takeoff weight: 14,750 lb (6,690 kg)
Powerplant : 2× General Electric T700 turboshaft, 1,680shp (1,300 kW) each
Rotor systems : 2 blades on main rotor, 2 blades on tail rotor
Performance
Maximum speed: 190 knots (218 mph, 352 km/h)
Range: 317 nm (365 mi, 587 km)
Service ceiling: 12,200 ft (3,720 m)
Rate of climb: 1,620 ft/min (8.2 m/s)
Armament
M197 3-barreled 20 mm "Gatling-style" cannon in the A/A49E-7 turret (750 rounds ammo capacity)
2.75 in (70 mm) Hydra 70 rockets Mounted in LAU-68C/A (7 shot) or LAU-61D/A (19 shot) launchers
5 in (127mm) Zuni rockets
8 rockets in two 4-round LAU-10D/A launchers
TOW Missiles
Up to 8 missiles mounted in
two-missile launchers on each hardpoint
AGM-114 Hellfire Missiles Up to 8 missiles mounted in
two 4-round M272 missile launchers, one on each outboard hardpoint
AIM-9 Sidewinder Anti-Aircraft Missiles
1 mounted on each outboard hardpoint (total of 2)
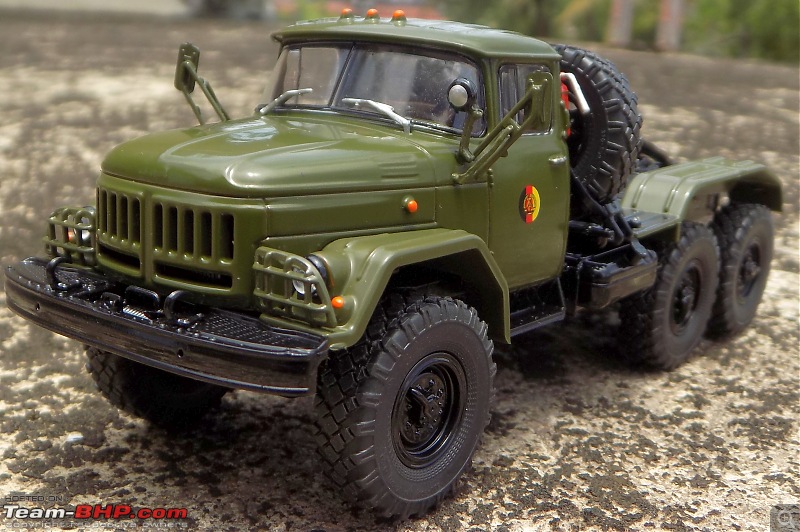
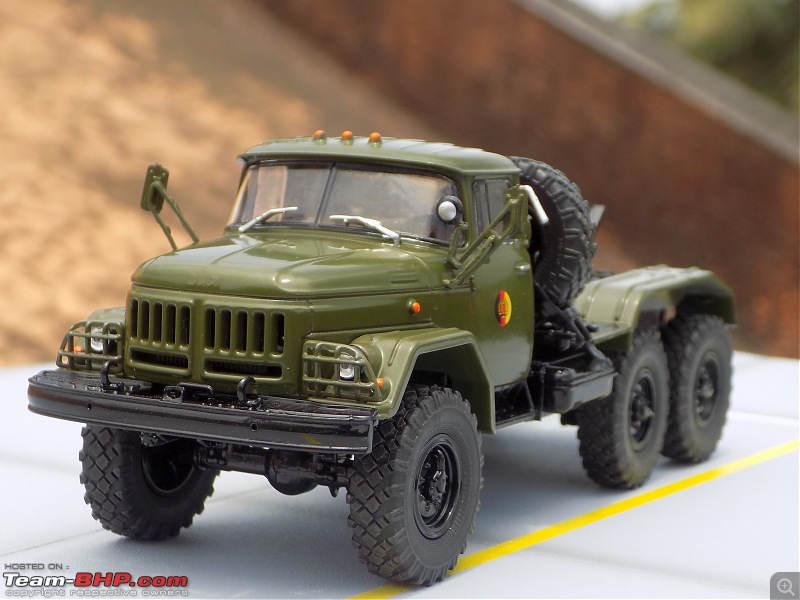
The model
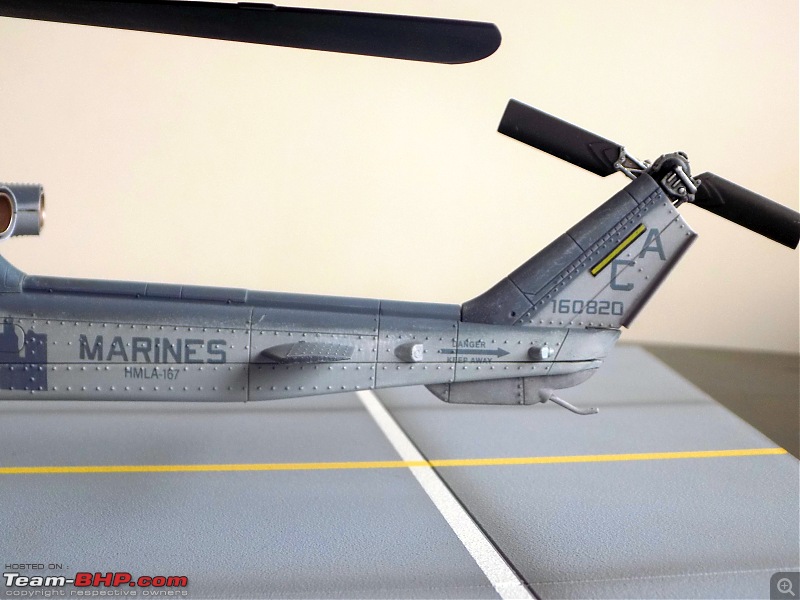
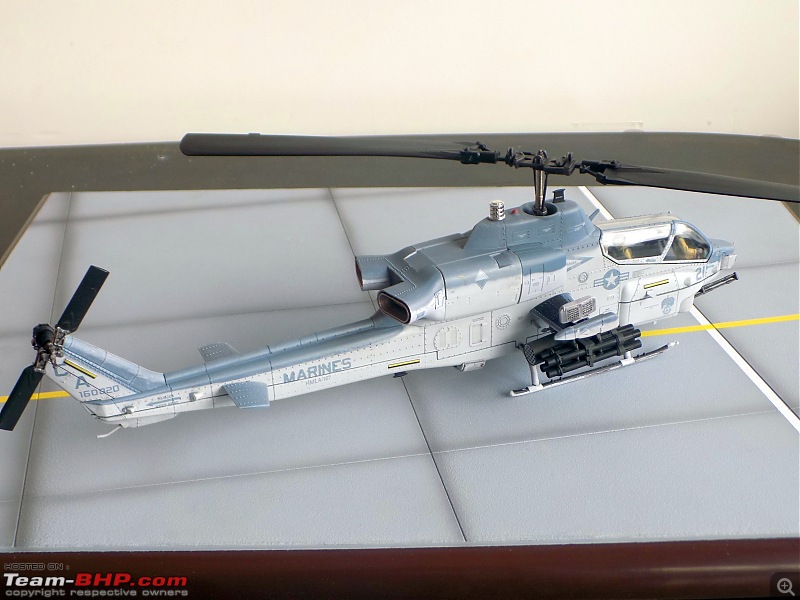
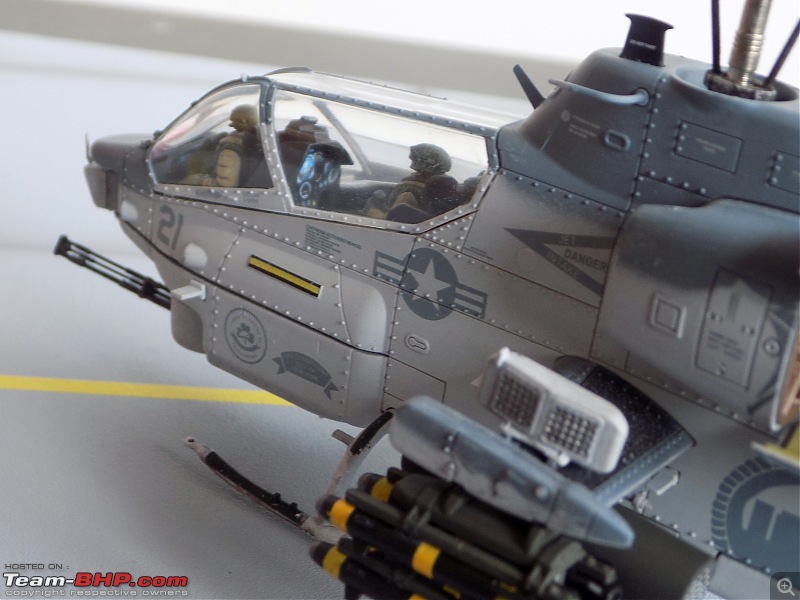
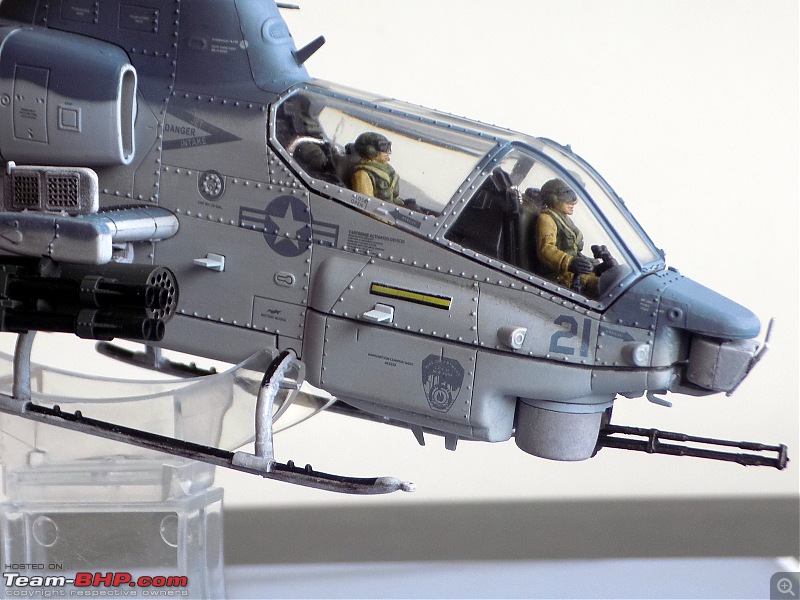
It's a beautiful model with insane amounts of detailing & wear & tear, as is evident from the photos.


9/11 tribute & Cobra markings replicated with stunning detail

The cannon turret & the M65 Laser Augmented Airborne TOW (LAAT) Sighting Unit are moveable. There is an option to fix individual rockets on the rocket pods but I was too lazy to do it

.
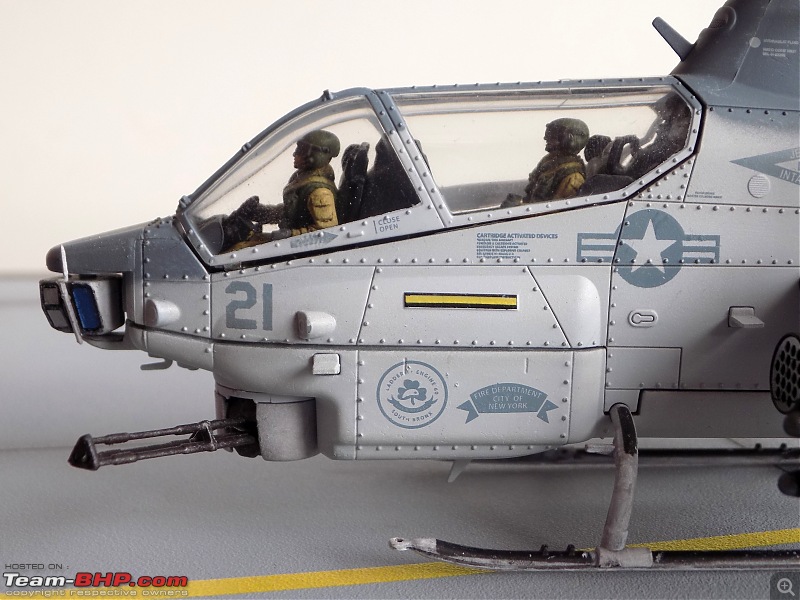





Engine Doors open to reveal intricate detailing on the "engines"
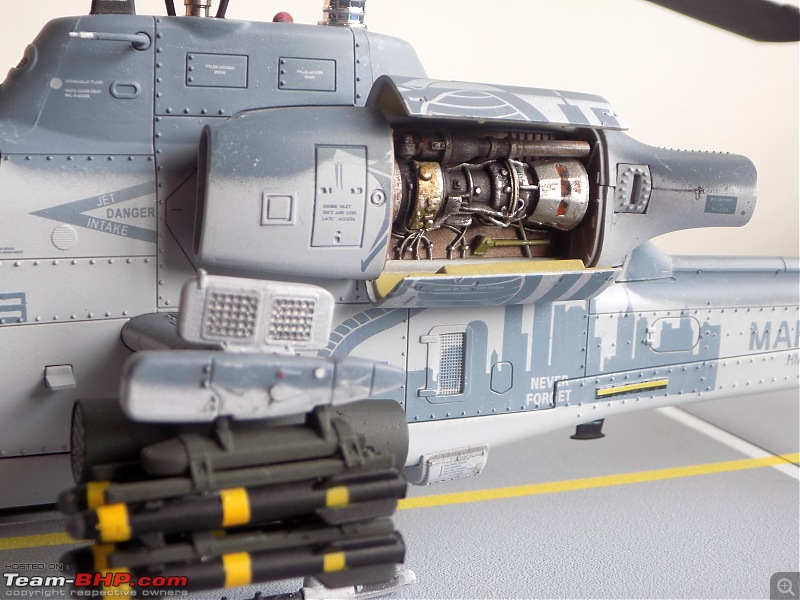
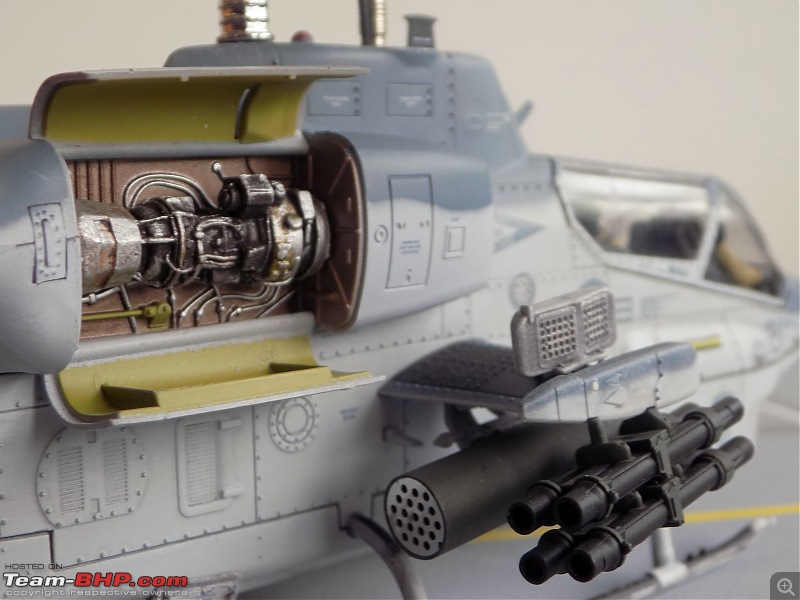


The Countermeasures dispenser above the stubby wings

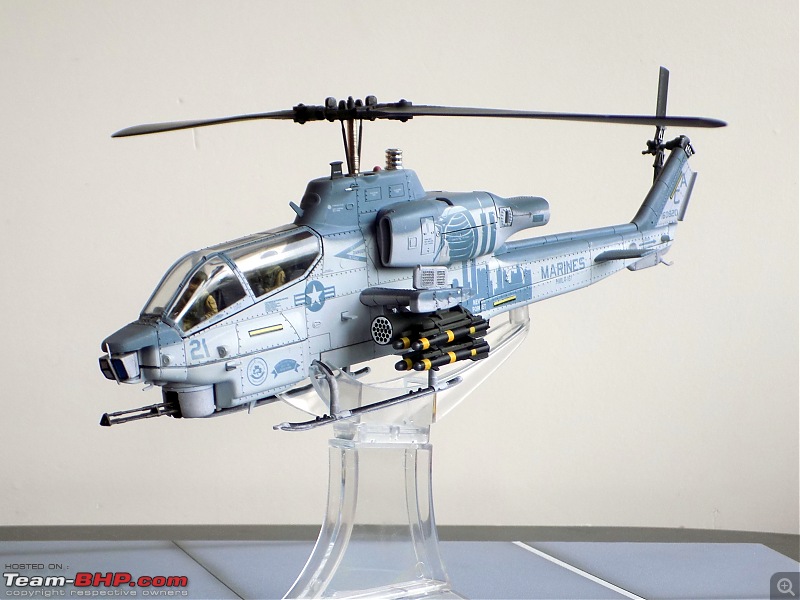
"In Flight"













The real helicopter





 (2)
Thanks
(2)
Thanks

 (1)
Thanks
(1)
Thanks

 (1)
Thanks
(1)
Thanks

 (4)
Thanks
(4)
Thanks
 (4)
Thanks
(4)
Thanks

 (1)
Thanks
(1)
Thanks
 (2)
Thanks
(2)
Thanks
 (1)
Thanks
(1)
Thanks
 (4)
Thanks
(4)
Thanks
 (4)
Thanks
(4)
Thanks

 (5)
Thanks
(5)
Thanks
 (2)
Thanks
(2)
Thanks
 (5)
Thanks
(5)
Thanks
 (3)
Thanks
(3)
Thanks
































 A grand display my friend.
A grand display my friend.


 .
.

























 .
.















