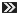|
The third-generation Toyota Corolla, built from 1974 to 1979 (worldwide versions) (KE3x/KE5x), marked Toyota's greatest growth in the United States in the wake of the fuel crisis. In addition to the Sprinter, there was a redesigned-body version built by Toyota affiliate Daihatsu, called the Daihatsu Charmant. While there were certain fourth-generation models with a longer model life, this generation, when considered as a whole, was the longest-lived one, possibly due to the worldwide recession in the 1970s. A large range of cars were built using this chassis, including Corollas, Sprinters, Daihatsu, and the sporty Levin and Trueno models with the DOHC motor.
The 3K engine was used in certain markets and later the 4K, while most Japanese and American models had the bigger 2T engine. A "Toyoglide" 2/3-speed automatic transmission was added as well as a four-speed and five-speed manual transmission, driving to the rear wheels. A three-door "liftback" (E50) and sports coupé (E51) was added in 1976. The E40 and E60 series were assigned to the Sprinter variants.
The 1.3 L (1290 cc) 4K was produced from 1978 through 1989. Cylinder bore was 75 mm (2.95 in) and stroke was 73 mm (2.87 in). It was a 8-valve OHV engine.
In 1980, the 4K produced 60 hp (45 kW) at RPM. From 1982 through 1984, output was 65 hp (48 kW) at 5600 RPM and 72 ft·lbf (97 N·m) at 3600 RPM.
The 1981 and 1982 California-spec 4K-C produced 58 hp (43 kW) at 5200 RPM and 67 ft.lbf (90 Nm) at 3600 RPM. Torque was up to 74 ft·lbf (100 N·m) at 3400 RPM for the fuel injected 1982 through 1984 4K-E. The Japan-spec 4K-U produced 74 hp (55 kW) at 5600 RPM and 78 ft·lbf (105 N·m) at 3600 RPM in 1982.
Source wikipedia. |